OpenAI has open-sourced again: launching two open-source models that can run on laptops and mobile phones.
On August 5 local time, OpenAI released its first open-source weight language models since GPT-2: gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b. These models match the performance of o4-mini and o3-mini and can run on high-end laptops and smartphones.
OpenAI is re-embracing open-source, with the company stating that one reason for releasing the open-source systems is that some businesses and individuals prefer to run such technology on their own computer hardware. “Open-source models complement our hosted models, providing developers with a richer selection of tools.” This helps accelerate cutting-edge AI research and lower barriers to entry for emerging markets, resource-constrained industries, and small organizations.
OpenAI President and co-founder Greg Brockman said, “If we provide a model, people will use our technology. They will rely on us to achieve the next breakthrough. They will provide us with feedback, data, and various information needed to improve the model. This helps us make further progress.”
Launching open-source models that can run on smartphones
The gpt-oss model is one of the first open-source weight language models released by OpenAI since the launch of GPT-2 in 2019. OpenAI stated that gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b push the boundaries of open-source weight inference models, outperforming similarly scaled open-source models in inference tasks, achieving practical application performance at low cost, and can be efficiently deployed on consumer-grade hardware after optimization. The model training process incorporates reinforcement learning techniques and draws inspiration from OpenAI's O3 and other cutting-edge internal models.
The GPT-OSS models utilize pre-training and post-training techniques, focusing on inference capabilities, efficiency, and practical usability across various deployment environments. Each model is based on the Transformer architecture and employs the Mixed Expert (MoE) technique to reduce the number of activation parameters required to process inputs. The gpt-oss-120b model activates 5.1 billion parameters per token, while the gpt-oss-20b model activates 3.6 billion parameters per token. The total parameters for the two models are 117 billion and 21 billion, respectively. They adopt an alternating dense and locally striped sparse attention pattern, similar to GPT-3. They support a context length of up to 128k using Rotated Position Encoding (RoPE). Both open-source models support three levels of inference strength—low, medium, and high—allowing developers to balance latency and performance. Developers can set the inference strength with a single line in the system message.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman stated that gpt-oss performs on par with o4-mini and can run on high-end laptops, while smaller versions can run on mobile phones. “In the near future, there will be something smarter than the smartest person you know, running on the device in your pocket, helping you solve various problems anytime, anywhere. This is truly an extraordinary thing.”
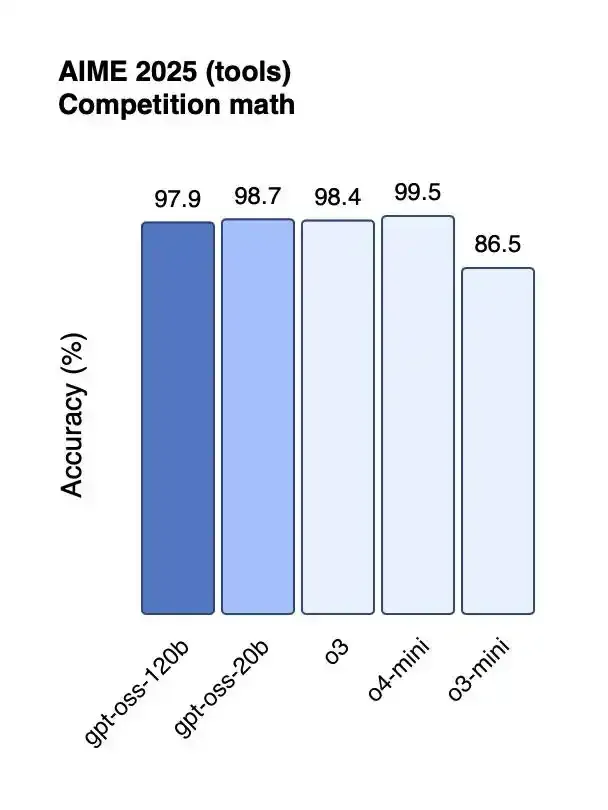
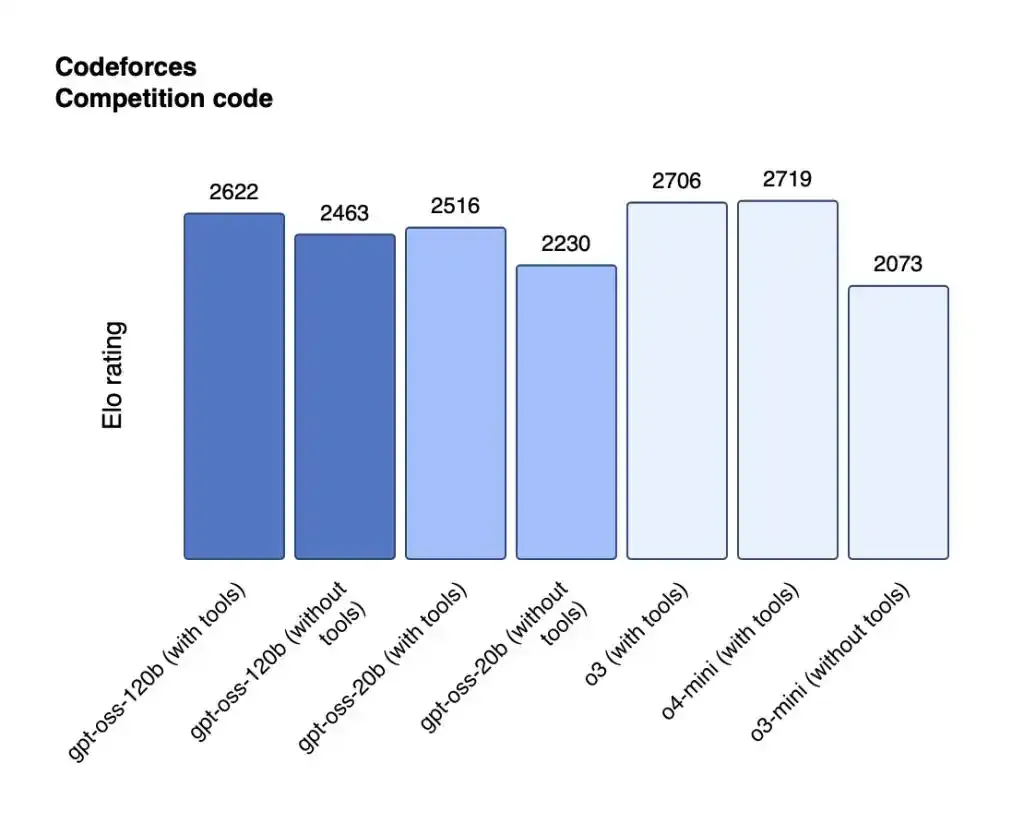
Performance of gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b in competitive programming.
The GPT-OSS-120B model performs nearly on par with OpenAI's O4-Mini on core inference benchmarks and can run efficiently on a single 80GB GPU. In competitive programming (Codeforces), general problem-solving (MMLU and HLE), and tool invocation (TauBench), the GPT-OSS-120B outperforms OpenAI's O3-Mini and matches or exceeds the performance of OpenAI's O4-Mini. In health-related queries and competitive mathematics, its performance is even better than o4-mini. The gpt-oss-20b model performs similarly to OpenAI o3-mini on common benchmarks, and even outperforms o3-mini in competitive mathematics and health-related queries, requiring only 16GB of memory to run on edge devices.
Why is OpenAI embracing open-source again?
Three years ago, OpenAI launched ChatGPT and sparked an AI boom. Since then, most of OpenAI's technology has remained under wraps. Other companies have shared their technology through “open-source” initiatives, encroaching on OpenAI's market share. The emergence of DeepSeek, in particular, has sparked a new wave of open-source initiatives worldwide. Now, OpenAI is re-embracing open-source to balance the competitive landscape and ensure that businesses and other software developers continue to use its technology. OpenAI stated that one reason for releasing the open-source system is that some businesses and individuals prefer to run such technology on their own computer hardware.
“Open-source models complement our hosted models, providing developers with a richer selection of tools,” OpenAI said. This helps accelerate cutting-edge research, spark innovation, and promote safer and more transparent AI development across various application scenarios. These open-source models also lower the barriers to entry for emerging markets, resource-constrained industries, and small organizations.
Recent research indicates that monitoring the thought chains of inference models can help detect inappropriate behavior, provided the models have not undergone direct supervised training for thought chain alignment. OpenAI noted that the thought chains of both GPT-OSS models have not received any direct supervision, which is critical for monitoring inappropriate behavior, deceptive outputs, and abuse risks in models. The release of two open-source models with unsupervised reasoning chains provides developers and researchers with the opportunity to study and build their own reasoning chain monitoring systems. Since reasoning chains may contain hallucinations or harmful content, developers should not directly display reasoning chain content to users in their applications.
To ensure model safety, OpenAI filtered out specific harmful data related to chemistry, biology, radiation, and nuclear matters during the pre-training phase. During post-training, it employed cautious alignment and instruction-level techniques to teach the model to reject unsafe prompts and defend against prompt injection attacks. After the open-source models are released, attackers may fine-tune the models for malicious purposes. To assess such risks, OpenAI fine-tuned the model using specific biological and cybersecurity data to simulate attacker behavior, creating a “non-rejection” version tailored to each domain, and evaluated the models' capability levels through internal and external testing. The tests showed that even when fine-tuned using OpenAI's industry-leading training stack, these maliciously fine-tuned models could not achieve high capability levels.
OpenAI stated that these processes mark a meaningful step forward in the security of open-source models, “We hope these models will help drive safe training and alignment research across the industry.” To build a safer open-source ecosystem, OpenAI launched a $500,000 “Red Team Challenge” to encourage researchers, developers, and enthusiasts worldwide to help identify new security issues.
The debate between open-source and closed-source continues, and corporate strategies are evolving. Unlike OpenAI's embrace of open-source, Meta may shift toward a more conservative closed-source software strategy. Following the establishment of its Superintelligence Lab, a small group of senior members discussed abandoning the company's most powerful open-source AI model, Behemoth, in favor of developing closed-source models.

